Definite Integrals (part 4) | Summary and Q&A
TL;DR
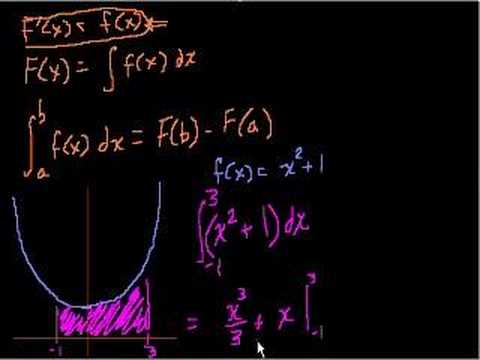
The fundamental theorem of calculus states that the definite integral of a function can be calculated by evaluating its antiderivative at the upper and lower limits. This allows for the calculation of areas between curves.
Key Insights
- 👻 Definite integrals allow for the calculation of areas under curves and between curves.
- ❓ The fundamental theorem of calculus relates the derivative and antiderivative of a function to the definite integral.
- 💁 The antiderivative of a function can have multiple possible forms, but the constant term does not affect the final result when calculating the definite integral.
- 😘 The definite integral of a function can be calculated by evaluating its antiderivative at the upper and lower limits.
- ❓ When calculating the area between two curves, the areas under each individual curve are calculated separately and then subtracted.
- 🟰 The antiderivative of a function can be found by finding a function whose derivative is equal to the given function.
- ◾ The definite integral can be viewed as a sum of infinitely small squares, representing the area under a curve.
Transcript
Welcome back. I'm now going to use definite integrals to figure out the areas under a bunch of curves and, if we have time, maybe even between some curves. So let me right down the fundamental theorem of calculus. I know I covered it really fast in the last presentation. Just to make sure you understand this formula. The last couple presentations w... Read More
Questions & Answers
Q: What does the fundamental theorem of calculus state?
The fundamental theorem of calculus states that if the derivative of a function is equal to the function itself, then the definite integral of the function can be calculated by evaluating its antiderivative at the upper and lower limits.
Q: How can the definite integral be used to calculate the area between a curve and the x-axis?
By finding the antiderivative of the function and evaluating it at the upper and lower limits, the definite integral gives the area between the curve and the x-axis.
Q: How can the area between two curves be calculated?
To calculate the area between two curves, the areas under each individual curve are calculated separately using the definite integral, and then the result of the second curve is subtracted from the result of the first curve.
Q: Why does the constant in the antiderivative not affect the final result?
When subtracting the antiderivative values at the upper and lower limits, the constants cancel out, so the exact value of the constant does not matter in calculating the definite integral.
Summary & Key Takeaways
-
The fundamental theorem of calculus states that if a function's derivative is equal to the function itself, then the definite integral of the function can be calculated by evaluating its antiderivative at the upper and lower limits.
-
The definite integral can be used to calculate the area between a curve and the x-axis.
-
To calculate the area between two curves, the areas under each curve are calculated separately and then subtracted from each other.
Share This Summary 📚
Explore More Summaries from Khan Academy 📚