Hess Law Chemistry Problems - Enthalpy Change - Constant Heat of Summation | Summary and Q&A
TL;DR
Hess's Law allows us to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by adding or modifying equations with known enthalpy values.
Key Insights
- 👻 Hess's Law allows us to predict the enthalpy change for a reaction by combining known reactions.
- ◀️ Multiplying or reversing a reaction affects the enthalpy change.
- 🎁 Species that are present in multiple reactions should be avoided when modifying equations.
- 💱 The enthalpy change for a reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes of the added or modified reactions.
- 🪘 Hess's Law applies to any chemical reaction, as long as we can find appropriate reactions to combine.
- 💱 The enthalpy change depends only on the initial and final states, not the specific pathway.
- ⚾ Hess's Law is based on the principle of energy conservation.
Questions & Answers
Q: What is the main idea behind Hess's Law?
Hess's Law states that we can use the enthalpy values of other reactions to predict the enthalpy change for a different reaction. By adding or modifying equations, we can cancel out common species and obtain the desired reaction.
Q: How does multiplying or reversing a reaction affect the enthalpy change?
If a reaction is multiplied by a factor, the enthalpy change is also multiplied by the same factor. Similarly, if a reaction is reversed, the sign of the enthalpy change will change from positive to negative or vice versa.
Q: How do we calculate the enthalpy change for a new reaction using Hess's Law?
We need to adjust the enthalpy values of the added or modified reactions and then sum them up. The adjusted values take into account factors such as multiplying, reversing, or canceling species.
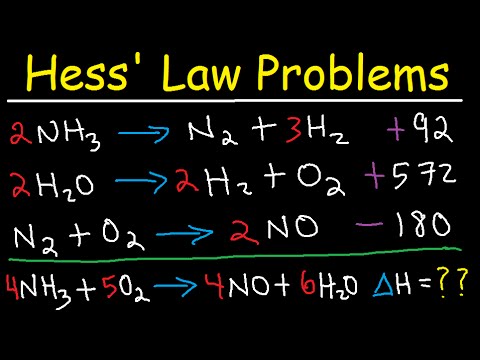
Q: Can you provide an example of using Hess's Law to calculate the enthalpy change?
Let's consider the reaction 2A + 2B -> 2C with an enthalpy change of 300 J and E -> C + D with an enthalpy change of -400 J. To calculate the enthalpy change for A + B + D -> E, we multiply the first reaction by 1/2, reverse the second reaction, and then add the enthalpy changes. The result is an enthalpy change of 550 J.
Summary & Key Takeaways
-
Hess's Law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction depends only on the initial and final states, not the specific pathway.
-
To use Hess's Law, we can add or modify reactions to cancel out common species and obtain the desired reaction.
-
The enthalpy change for the desired reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes of the added or modified reactions.
Share This Summary 📚
Explore More Summaries from The Organic Chemistry Tutor 📚