Ep. 2: What the Universe Is Made of | Summary and Q&A
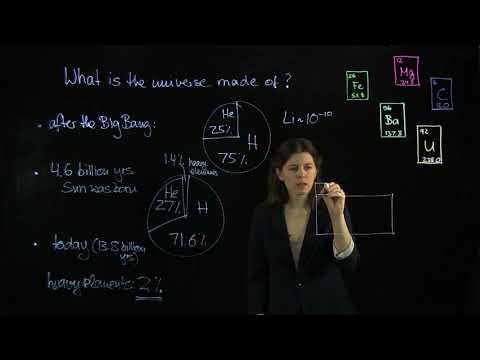
TL;DR
This content explores the composition of the universe at different times, highlighting that hydrogen and helium are the most abundant elements, while heavy elements make up a small fraction.
Key Insights
- 🇧🇩 The universe was primarily composed of hydrogen and helium after the Big Bang.
- ❗ The Sun's formation marked a shift in the universe's composition, with more helium and the emergence of heavy elements.
- ❣️ Heavy elements, although a small fraction, play a crucial role in the composition of the universe today.
- 😒 Astronomers use the term "metals" to refer to all elements besides hydrogen and helium.
Transcript
Have you ever wondered how all the chemical elements are made? Then join me as we are lifting all the star dust secrets to understand the cosmic origin of the chemical elements. What is the universe actually made off? Let's look at three different times in the universe and consider what it was made of. First after the Big Bang. So if we draw a litt... Read More
Questions & Answers
Q: What were the main elements present in the universe after the Big Bang?
After the Big Bang, the universe was primarily made up of hydrogen (75%), helium (25%), and a small amount of lithium.
Q: What changes occurred in the composition of the universe 4.6 billion years after the Big Bang?
At that time, the universe had slightly less hydrogen, more helium (70.6%), and a small percentage (1.4%) of heavy elements formed from the conversion of helium.
Q: How much of the universe is made up of heavy elements today?
Today, heavy elements make up 2% of the universe, while hydrogen and helium remain the majority.
Q: How can studying the chemical composition of stars help understand the cosmic origin of elements?
Stars reflect the composition of the gas clouds they formed from, so studying the chemical composition of stars born at different times can provide insights into how the composition of the universe changed over time.
Summary & Key Takeaways
-
The universe after the Big Bang consisted mostly of hydrogen and helium, with a small amount of lithium.
-
4.6 billion years later, the Sun was born, and the composition of the universe included less hydrogen, more helium, and a small percentage of heavy elements.
-
Today, heavy elements make up 2% of the universe, with hydrogen and helium still being the most abundant elements.
Share This Summary 📚
Explore More Summaries from MIT OpenCourseWare 📚