Antiparallel structure of DNA strands | Biology | Khan Academy | Summary and Q&A
TL;DR
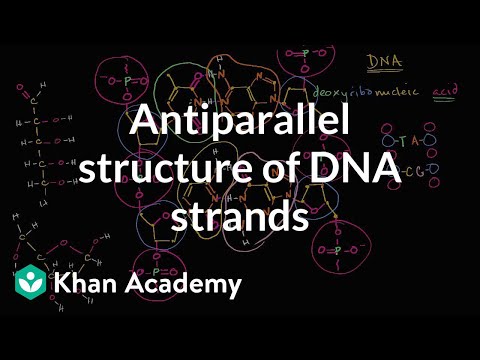
DNA is made up of two strands with phosphate-sugar backbones and nitrogenous bases forming complementary pairs. The structure is antiparallel, with phosphate groups repelling each other and hydrogen bonds attracting the nitrogenous bases.
Key Insights
- 🧬 DNA has a molecular structure consisting of two strands with phosphate-sugar backbones and nitrogenous bases.
- 💁 The nitrogenous bases (thymine, adenine, cytosine, guanine) form complementary pairs through hydrogen bonding.
- ❓ The structure of DNA is antiparallel, with the strands oriented in opposite directions.
- 😐 The phosphate groups in DNA are acidic and can be protonated, but they tend to be deprotonated in neutral conditions.
- 🥺 The repulsion between phosphate groups leads to the formation of the ladder-like structure of DNA.
- 🌥️ The DNA molecule is long and contains a large number of base pairs.
- 🧬 The hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases provide stability to the DNA structure.
Transcript
- [Voiceover] In the video on the molecular structure of DNA we saw that DNA is typically made up of two strands where the backbone of each of the strands is made up of phosphate alternating between a-- Do some different colors. A phosphate group and then you have a sugar. You have a phosphate group. And then you have a sugar. And then you have a p... Read More
Questions & Answers
Q: Why is DNA called an acid?
DNA is called an acid because its phosphate groups can act as acids when protonated. However, in neutral solutions, these groups tend to be deprotonated, which is why they are drawn that way.
Q: How do the nitrogenous bases form the rungs of the DNA ladder?
The nitrogenous bases form the rungs of the DNA ladder through hydrogen bonding. The partially negative and positive charges on the bases attract each other, creating stable pairs.
Q: Why are the two strands of DNA considered antiparallel?
The two strands of DNA are considered antiparallel because they have opposite orientations. The sugars on one strand have the oxygen pointing up, while on the other strand, the oxygen points down.
Q: What role do phosphate groups play in the structure of DNA?
The phosphate groups in DNA have a negative charge and repel each other. This repulsion leads to the strands orienting themselves in a way that maximizes the distance between the phosphate groups.
Summary & Key Takeaways
-
DNA consists of two strands, each with a backbone made up of alternating phosphate and sugar molecules.
-
The nitrogenous bases, thymine, adenine, cytosine, and guanine, form pairs through hydrogen bonds.
-
The structure of DNA is antiparallel, with the two strands oriented in opposite directions.
Share This Summary 📚
Explore More Summaries from Khan Academy 📚